# Robust Adversarial Perturbation
Robust Adversarial Perturbation on Deep Proposal-based Models.
🌏 Source
🔬 Downloadable at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.05962. CVPR 2020.
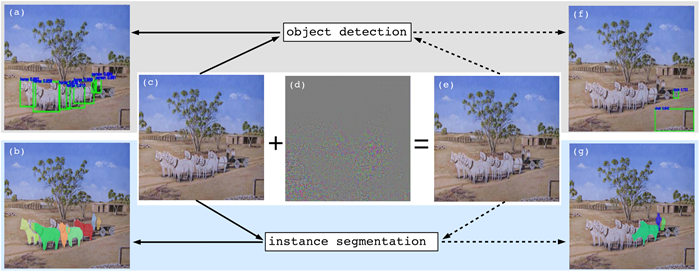
R-AP stands for robust adversarial perturbations. R-AP focuses on attacking RPNs, namely: Region Proposal Networks, to universally degrade the performance of object detection and instance segmentation algorithms.
The research on R-AP is the first work to thoroughly investigate the effects of adversarial perturbation on RPNs.
# Main contributions
Attack targets:
- Deep proposal-based object detectors
- Instance segmentation algorithms
Focuses on: RPN, Region Proposal Networks.
Algorithm: designed a loss function that combines (i) label loss and (ii) shape loss, each of which targets a specific aspect of RPN. In contrast to previous attack paradigms that only disturb object class label predictions, our method not only disturbs the proposal label prediction in RPN, but also distracts the shape regression, which can explicitly degrade the bounding box prediction in proposal generation.
# R-AP features
R-AP method focuses on attacking deep proposal-based models that are fundamental to majority of object detectors and instance segmentation algorithms. A majority of object detectors and instance segmentation algorithms use a Region Proposal Network (RPN) to extract object-like regions, known as proposals, from an image and then process the proposals further to obtain:
- object class labels and bounding boxes in object detection, and ...
- ... the instance class labels and region masks in instance segmentation.
If a RPN is successfully attacked by an adversarial perturbation, such that no correct proposals are generated, the subsequent process in the object detector and instance segmentation pipeline will be affected by design.
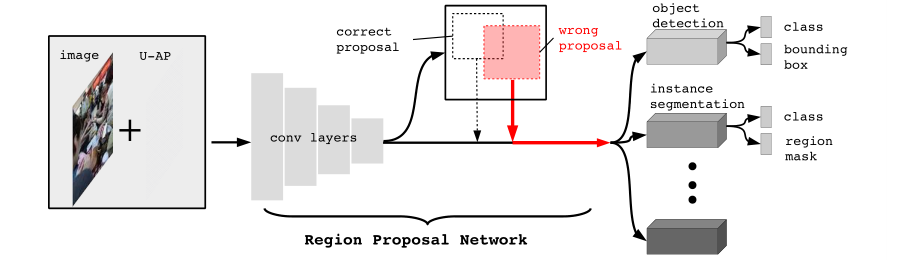
# Methods
All mainstream deep proposal-based object detectors and instance segmentation algorithms rely on a few standard RPNs to provide proposals for subsequent processes. Once the RPN is disturbed, the performance of these deep models is naturally degraded. As such, our R-AP method is suitable in nature for black-box attack to these models, i.e., without the need to know their implementation details.
# Loss function
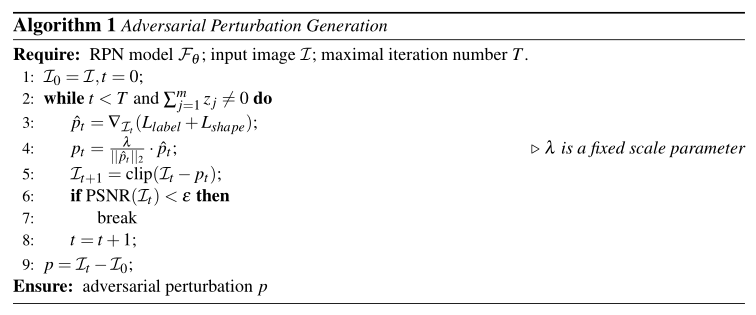
R-AP's goal is to seek an minimal adversarial perturbation added to image
- The label loss
- The shape loss
Finally, the R-AP algorithm generates a perturbed image
# Label loss
The label loss
In other words, minimizing this loss is equivalent to decreasing confidence score of positive proposals.
# Shape loss
The goal of shape loss is to explicitly disturb the shape regression.
where
# Algorithm
The R-AP generation algorithm:
# Experiments
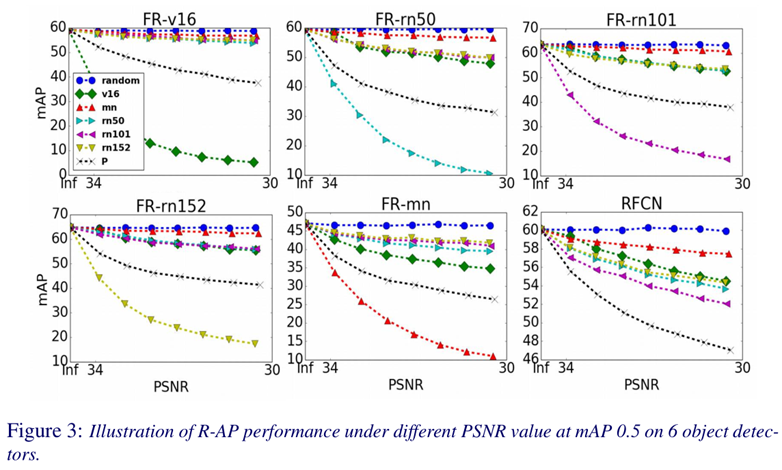
The R-AP method is evaluated on the MS COCO 2014 dataset.
# Object detection
# Image / Instance segmentation
# Sample images
Visual results of the R-AP attack on several mainstream object detectors (first 4 rows) and instance segmentation algorithms (last 2 rows):

# Conclusions
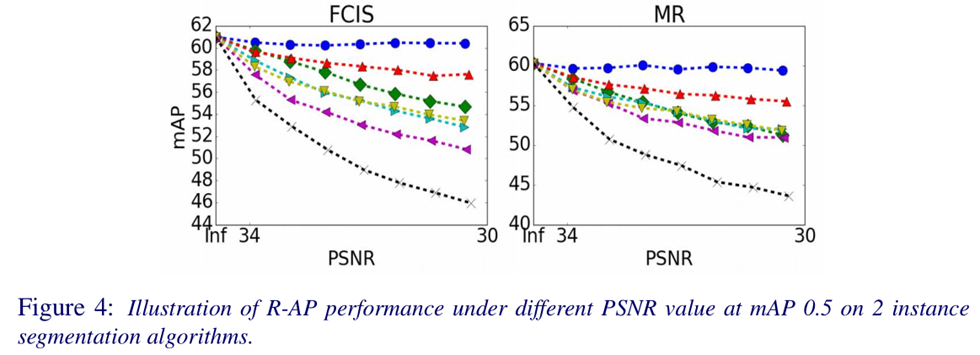
The R-AP method designed a new loss function to not only disturb label prediction but also degrade shape regression. The design of shape loss and the use of PSNR is worth noticing.
# Referred in
- papers
- | Paper Title | Publication | | invisible-adv | IEEE 2019 | | robust-adversarial-perturbation | CVPR 2020 | | perceptual-color-distance | CVPR 2020 | | adversarial-camouflage | CVPR 2020 |